Space Industry Technical Standards
To foster economic growth and technological advancement of the U.S. commercial space industry, the Office of Space Commerce (OSC) participates in the development and promotion of space technical standards by standards development organizations and by coordination groups led by government agencies and trade organizations. OSC is particularly involved in standards related to space situational awareness (SSA) data sharing and coordination, which is essential to the Traffic Coordination System for Space (TraCSS).
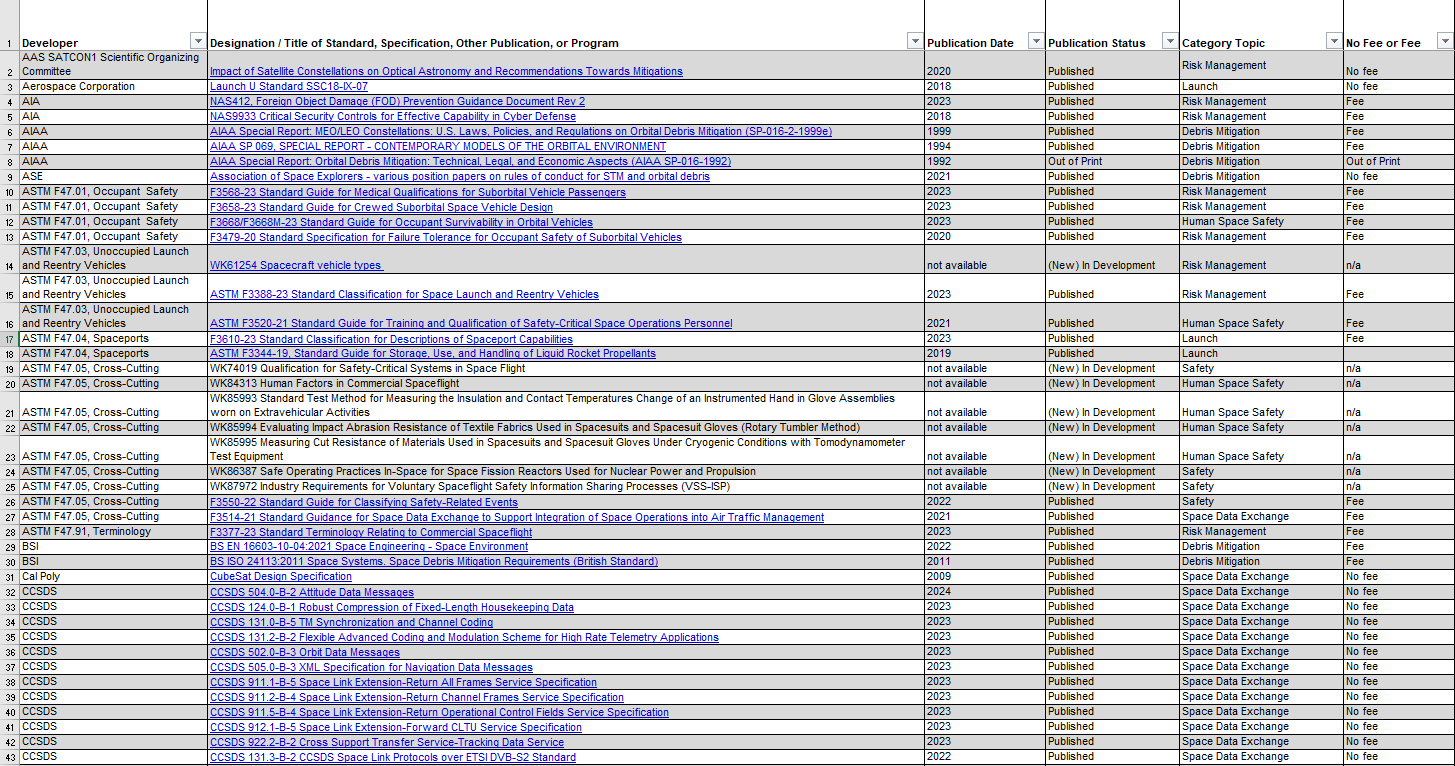
This page hosts the Space Industry Technical Standards Compendium, a curated reference spreadsheet of space standards in use today or in development. This page also provides background information on space standards organizations and the U.S. government’s use of standards. The Compendium was last updated in June 2024.
Standards Compendium
The Office of Space Commerce developed this spreadsheet to provide the public with an easy-to-use, searchable summary of space standards.
- Space Industry Technical Standards Compendium, June 2024 (PDF)
- Space Industry Technical Standards Compendium, June 2024 (Excel format)
- Space Industry Technical Standards Compendium, June 2024 (Online database)
OSC will continuously update the compendium. We welcome feedback on the use of specific standards and of the spreadsheet: Contact us
Background on Space Standards
What are space standards?
Space standards are guidelines, best practices, and recommendations that describe the specifications, dimensions, and requirements for designing and operating equipment, and systems in space. These help ensure the safety, reliability, and compatibility of space missions and activities within and across organizations, as well as facilitate international cooperation and coordination.
Space standards are vital for the design, operation, and success of space missions and activities. They provide a common language and framework for space agencies and organizations across the globe, enabling them to work together and achieve their goals. By following standards, space professionals can ensure the safety, reliability, and compatibility of space systems in a safe and sustainable manner.
How are space standards developed?
Standards are often developed via consensus building on what the standard addresses, most often through international standards developing organizations, such as the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), the Consultative Committee for Space Data Systems (CCSDS), or ASTM International. Standards from these organizations are voluntary consensus standards and are usually appropriate or adaptable for the government’s purposes.
The CCSDS is a multi-national organization of international space agencies and develops open communications and data standards for space systems. CCSDS has multiple working groups developing and publishing standards. The Navigation Working Group family of space data messages are most applicable to be used by space launch operators, spacecraft operators, SSA service data providers, analysts, and message exchange partners and are freely accessible at the CCSDS website.
ISO is a multi-national forum that enables the development and publication of international standards through its members by bringing together experts to share knowledge and develop voluntary, consensus-based, market relevant international standards. Technical Committee (TC) 20, Aircraft and Space Vehicles has subcommittees (SC) focused on the standardization of materials, components and equipment for construction and operation of aircraft and space vehicles as well as equipment used in the servicing and maintenance of these vehicles. TC 20 has to-date published 682 ISO standards with 17 participating member countries and 28 observing member countries. There are two subcommittees supporting space data messaging and SSA: SC 13 Space data and information transfer systems and SC 14 Space systems and operations. Products from SC 13 are identical to products from the CCSDS via formal arrangements between ISO and CCSDS.
In addition, government agencies, such as NASA, National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), and European Space Agency (ESA), and professional and trade organizations, such as SAE International, develop standards specific to technical disciplines as required for their needs and trade, usually through consensus building processes with their stakeholders.
How does the U.S. Government use standards?
OMB Circular A-119, revised by the Office of Management and Budget (OMB) in January 2016, spells out the government strategy for standards development. It promotes agency participation on standards bodies, specifies reporting requirements on conformity assessment activities, and informs agencies of their statutory obligations related to standards setting. Visit the NIST website for more information.
As described in OMB Circular A-119, the use of standards for the government’s purposes, whenever practicable and appropriate, is intended to achieve the following goals:
- eliminating the cost to the Federal government of developing its own standards and decreasing the cost of goods procured and the burden of complying with agency regulation;
- providing incentives and opportunities to establish standards that serve national needs, encouraging long-term growth for U.S. enterprises and promoting efficiency, economic competition, and trade; and
- furthering the reliance upon private sector expertise to supply the Federal government with cost-efficient goods and services.



